What is the purpose of a screening test?
Friday May-16 2025 16:53:52
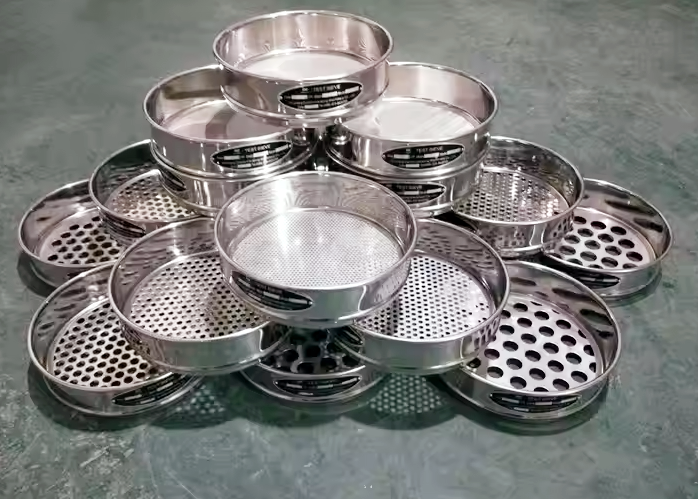

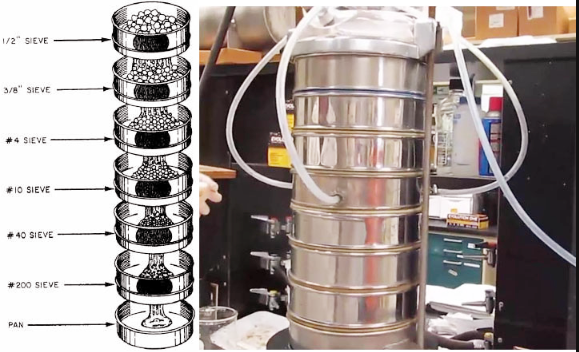
The screening test is to separate and grade the granular materials according to the particle size by using sieves with different apertures to determine the particle size distribution characteristics of the material. Its core purpose is to determine the particle size distribution of the material, and on this basis evaluate the relevant performance of the material or guide production practice.
1.Determine particle size distribution

Pour material samples (such as sand, gravel, soil, etc.) into a series of standard sieves with apertures from large to small (such as square hole sieves, round hole sieves) for screening, weigh the mass of the material retained on each sieve layer, calculate the proportion (percentage) of each particle size, and thus determine the distribution of material particle size.
Application scenario: Determine whether the material meets the engineering standards (such as concrete aggregates, roadbed fillers, etc.) to ensure that its physical properties meet the requirements.
In the construction industry, it is used to analyze the particle size distribution of aggregates such as sand, gravel, and cement to determine whether they meet the design requirements of concrete, mortar, etc.
In the field of mineral processing, it is used to evaluate the particle size composition of ore after crushing or grinding, and guide the adjustment of mineral processing process parameters.
In the chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries, it is used to detect whether the particle size of powdered raw materials or products is uniform and whether it meets the production process or quality standards (such as the coarseness of flour and the dispersibility of drug particles).
2. Evaluate the physical properties of materials
Particle grading directly affects many physical properties of materials, and screening tests can indirectly reflect these properties:
① Particle uniformity: If the material particle grading is concentrated (such as most particles are concentrated in a certain screen layer), it means good uniformity; if the particle distribution range is wide (across multiple screen layers), the uniformity is poor.
② Packing density and void ratio: The more reasonable the particle grading (such as the appropriate combination of large and small particles), the lower the void ratio during stacking and the higher the packing density. For example, if the concrete aggregate is well graded, the amount of cement can be reduced and the strength can be improved.
③ Fluidity: Too high a content of fine particles (such as clay and dust) may cause the material to stick together and reduce fluidity; too much coarse particles may affect the transportation or processing efficiency.
Soil permeability and compressibility (soil mechanics)
Material fluidity and bulk density (powder engineering)
Catalyst active surface area (chemical industry)
3.Guide production process optimization

Soil improvement: If the natural soil material is poorly graded (such as too coarse or too fine), the grading can be adjusted by mixing other materials.
Adjust crushing/grinding equipment parameters: Determine the working efficiency of crushing or grinding equipment based on the screening results. For example, if the proportion of material in a certain screen layer is abnormally high, it may be necessary to adjust the screen size of the crusher or the speed of the grinder.
Mixture ratio design: When materials of different particle sizes need to be mixed (such as asphalt mixtures, refractory materials), screening tests can help determine the proportions of each component to achieve optimal performance. In concrete or asphalt mixtures, a combination of aggregates of different particle sizes needs to be selected through screening tests to optimize density, strength and durability.
4.Other application scenarios

Environmental monitoring: Analyze the particle size distribution of particulate pollutants such as soil and dust, and evaluate their impact on the environment or human health (such as the ratio of PM2.5 to coarse particles).
Research and teaching: In research in the fields of materials science and mineral processing, screening tests are a common means of analyzing the basic properties of granular materials and are used to compare the effects of different processes or formulations.








